
| HOME |

|
ABOUT THE AUTHOR |

|
|

|
WHERE TO BUY |


Analysis of the movement of money forms Part I.
Part IV. Turning to the analysis of Article 128 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, we will move away from the fact that the following arises from the economic nature of money: it is not possible to talk about the legal nature of money in general. It is only possible to talk about the legal nature and corresponding legal regime of a concrete type of legal property goods, which carries out the function of money180 By analysing the table of the forms of money (see table 3), the table
of the material and liability content of different forms of money (see
table 7) and also the corresponding graphs, it is possible to come to the
conclusion there is an evolutionary ousting of one form of money by
another more suited to the corresponding level of industrial relations
and in contemporary economics literally all types of money exist, having,
however, varying degrees of prevalence in economic relations. Likewise it is necessary to point out, in accordance with M.A. Portnoy,
that different forms of money have different abilities to fulfil the
functions of money. For example, banknotes are an inadequate means
of preserving value (accumulation), nominal credit bills are not quite
suitable as a means of circulation, and financial money is inadequate
both as a means of circulation and as a means of payment. At the same
time, all of these are adequate as a measure of value181. It is particularly worth noting the following tendencies:
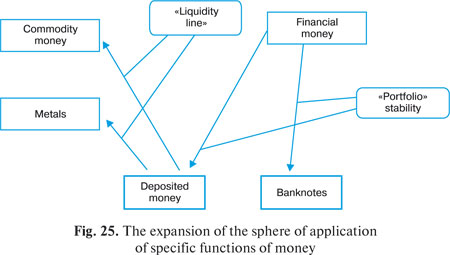 the development of commercial markets and electronic systems of
accessing natural products markets, and likewise the use of the «liquidity
line» as a mechanism distinctive to deposited money, in the
sector of contracts relating to stocks and shares, allows investment
funds to retain an essential part of their assets in exchange traded
commodities (ETCs), such as of oil products, light and dark metals
and even concentrated orange juice, which again endows commodity
money with the function of accumulation (fig. 25). The signing of international deals, such as, for example, «oil for
supply of provisions» between Iraq and the international community,
the acquisition of Russian credits by Iraq with oil and oil products;
«gifts» in the form of trains full of oil products to government officials
of several developing countries — finds us drawing a conclusion that a
certain tendency has taken shape, i.e. certain ETCs are acquiring the
function of circulation and, consequently, developing into money. Such ETCs in circulation take the following forms:
Thus, it is possible to establish that the historical spiral development
of forms of money results in all types of existing money advancing to a
new level. At present, forms of money which are of a liability nature, serve the
overwhelming majority of deals. Applying to them object/material rules
of circulation is not only unacceptable, but also creates huge problems
in the circulation of money, and consequently negatively affects the
credit-monetary system and the development of economics as a whole. Many lawyers confirm, that one or another form of money inadequately fulfils one or another function of money. In particular, there is much criticism of the fulfilment of the function of payment by securities. Here we once again emphasise that not one form of money ideally fulfils any one function (table 9). Fulfilment of the money functions by different forms of money in Russia 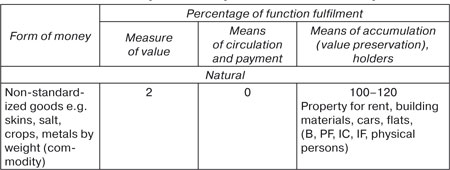 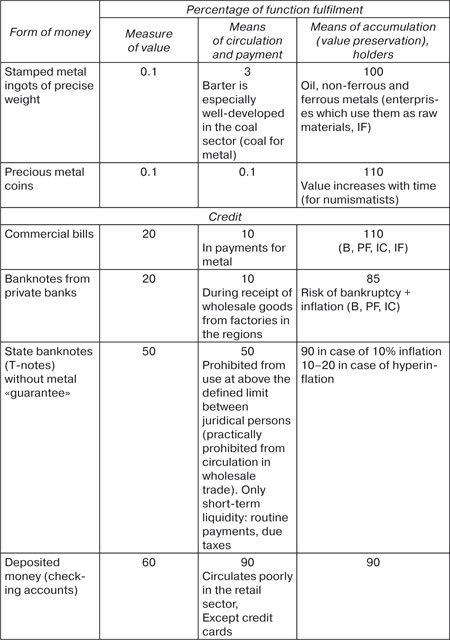 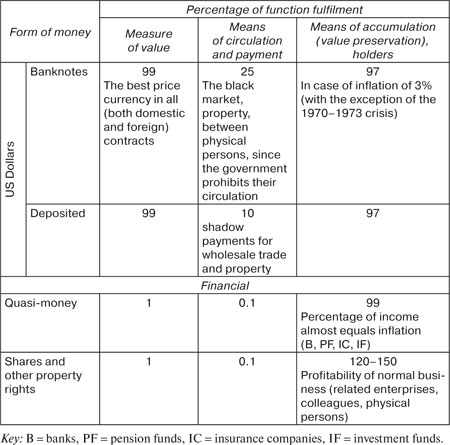 |
Copying information from this website is only allowed under condition of referring to this web link.
Copyright © 2008 Andrey Gribov
All rights reserved